Thames & Kosmos Physics Pro handleiding
Handleiding
Je bekijkt pagina 6 van 9
Pressure is force per unit of area
At every location of a liquid or a gas — including in water or the air
— there is a certain pressure. Let us first define pressure a little
imprecisely: There is a prevailing pressure when a force is evenly
distributed over a surface area. The larger the surface area, the
lower the pressure, and vice-versa.
How would a physicist say this more precisely? Pressure is the ratio
of a force exerted perpendicularly on a surface to the size of this
surface. In other words, force divided by area.
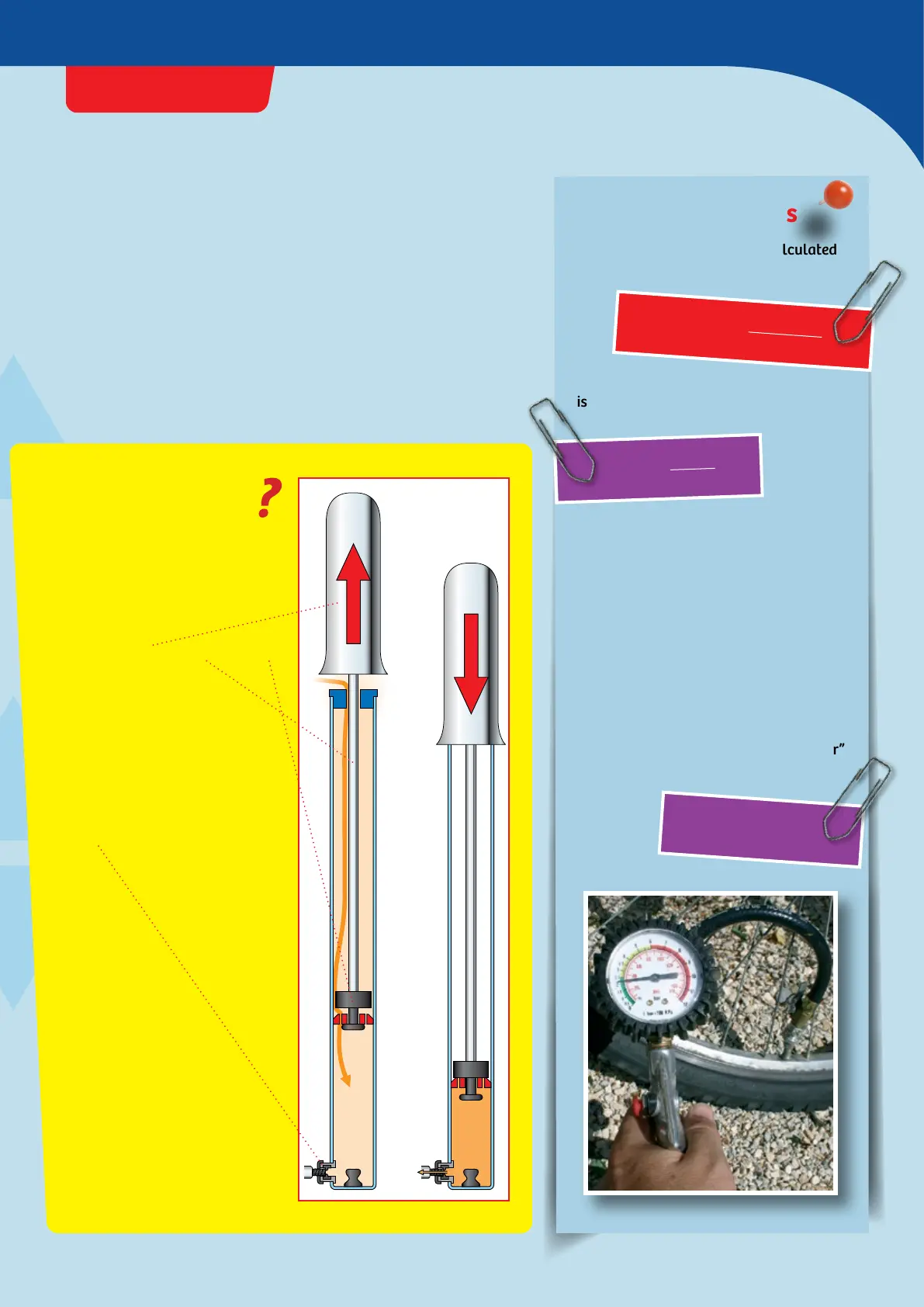
If you want to pump up a bicycle
tire, you grab an air pump. And
what does it do? It transfers the
force of your arm by way of the
pump handle and rod to a piston
which compresses the air that
had been sucked into the pump’s
pressure chamber.
The same pressure prevails
everywhere in the pressure
chamber. This pressure pushes
the air out of the pump through a
valve into the inner tube (or
tubeless tire).
The valve ensures that the air
only flows in one direction, into
the tube and not back. The tube
only gets air if the pressure in
the pump is greater than that in
the tube, because a liquid or gas
always moves from higher to
lower pressure. You will notice
while you pump that you need
more and more force. That is
because, as you pump, the
pressure in the tire increases.
IMPORTANT FORMULAS
PRESSURE Pressure can be calculated
by dividing force by area.
PASCAL The unit of measure for pressure
is 1 pascal (Pa), which is calculated as:
For high pressures, the numbers quickly
become very long. To save yourself from
writing all the zeros, it is easier to write
2,000 hectopascals (hPa) or, even more
briefly, 200 kilopascals (kPa). The “h” in
the abbreviation stands for “hecto” or
hundred-fold, the “k” for “kilo” or
thousand-fold.
BAR Many pressure gauges (manometers)
also have a different scale with the “bar”
pressure unit:
HOW DOES A BICYCLE
PUMP WORK
19
GOOD TO KNOW
Air and Water Under Pressure
1 N =
1 kg · m
s
2
1 Pa =
1 bar = 1,000 hPa
1 N
1 m
2
1 W =
1 J
1 s
P (Pressure) =
F
1
: A
1
= F
2
: A
2
p
1
: p
2
= V
2
: V
1
p
1
: p
2
= T
1
: T
2
or: p · V = constant
(only valid when T = constant)
F
1
· L
1
= F
2
· L
2
p
1
· V
1
= p
2
· V
2
A
1
· v
1
= A
2
· v
2
Load · Load arm = Force · Force arm
F (Force)
A (Area)
P (power) =
W (work) = F (force) · s (distance)
W (work)
t (time)
F
d
=C
d
·
A · · v
2
2
P == 2= 2 Pa
10 N
5 m
2
N
m
2
P == 200,000 Pa
100 N
0.0005 m
2
P =
= 16,000 Pa or 16 hPa or 1.6 bar
4 N
0.00025 m
2
or = constant=
p
1
· V
1
T
1
p · V
T
p
2
· V
2
T
2
F
d
= 0.4 ·
2 m
2
· 1.23 kg/m
3
· (40 m/s)
2
2
F
d
= 0.4 ·= 787.2 N
3936
2
kg · m
s
2
1 N =
1 kg · m
s
2
1 Pa =
1 bar = 1,000 hPa
1 N
1 m
2
1 W =
1 J
1 s
P (Pressure) =
F
1
: A
1
= F
2
: A
2
p
1
: p
2
= V
2
: V
1
p
1
: p
2
= T
1
: T
2
or: p · V = constant
(only valid when T = constant)
F
1
· L
1
= F
2
· L
2
p
1
· V
1
= p
2
· V
2
A
1
· v
1
= A
2
· v
2
Load · Load arm = Force · Force arm
F (Force)
A (Area)
P (power) =
W (work) = F (force) · s (distance)
W (work)
t (time)
F
d
=C
d
·
A · · v
2
2
P == 2= 2 Pa
10 N
5 m
2
N
m
2
P == 200,000 Pa
100 N
0.0005 m
2
P =
= 16,000 Pa or 16 hPa or 1.6 bar
4 N
0.00025 m
2
or = constant=
p
1
· V
1
T
1
p · V
T
p
2
· V
2
T
2
F
d
= 0.4 ·
2 m
2
· 1.23 kg/m
3
· (40 m/s)
2
2
F
d
= 0.4 ·= 787.2 N
3936
2
kg · m
s
2
1 N =
1 kg · m
s
2
1 Pa =
1 bar = 1,000 hPa
1 N
1 m
2
1 W =
1 J
1 s
P (Pressure) =
F
1
: A
1
= F
2
: A
2
p
1
: p
2
= V
2
: V
1
p
1
: p
2
= T
1
: T
2
or: p · V = constant
(only valid when T = constant)
F
1
· L
1
= F
2
· L
2
p
1
· V
1
= p
2
· V
2
A
1
· v
1
= A
2
· v
2
Load · Load arm = Force · Force arm
F (Force)
A (Area)
P (power) =
W (work) = F (force) · s (distance)
W (work)
t (time)
F
d
=C
d
·
A · · v
2
2
P == 2= 2 Pa
10 N
5 m
2
N
m
2
P == 200,000 Pa
100 N
0.0005 m
2
P =
= 16,000 Pa or 16 hPa or 1.6 bar
4 N
0.00025 m
2
or = constant=
p
1
· V
1
T
1
p · V
T
p
2
· V
2
T
2
F
d
= 0.4 ·
2 m
2
· 1.23 kg/m
3
· (40 m/s)
2
2
F
d
= 0.4 ·= 787.2 N
3936
2
kg · m
s
2
Bekijk gratis de handleiding van Thames & Kosmos Physics Pro, stel vragen en lees de antwoorden op veelvoorkomende problemen, of gebruik onze assistent om sneller informatie in de handleiding te vinden of uitleg te krijgen over specifieke functies.
Productinformatie
| Merk | Thames & Kosmos |
| Model | Physics Pro |
| Categorie | Niet gecategoriseerd |
| Taal | Nederlands |
| Grootte | 6755 MB |







