Holzmann EISA160-MINI handleiding
Handleiding
Je bekijkt pagina 26 van 35
OPERATION
HOLZMANN MASCHINEN GmbH www.holzmann-maschinen.at 26
EISA160MINI
OPERATION
15.1 Basic knowledges
Basically, welding is divided into two types of processes: fusion joint welding (joint without force)
and pressure joint welding (joint with force). In fusion welding, two workpieces (usually metals of
the same kind) are melted at the joints and joined with or without the addition of filler materials.
The energy required for this is supplied from outside. The most common fusion welding processes
include electrode welding (MMA) and shielding gas welding (TIG/WIG, MIG, MAG).
Before starting work, thoroughly remove rust and paint from the workpieces and grind them
bright. Then place the parts to be welded together (if necessary, fix them with gripping pliers or a
screw clamp) and attach the earth cable to a bare spot on the workpiece. First weld the seams
with spots only - this way you can still correct the position of the parts if necessary and still prevent
the material from warping due to the heat of the arc by fixing the spots. After you have removed
the slag from the welding spots, weld the seams through.
Note: Slag will form along the weld and you will have to tap or grind it off. If the weld seam is only
slightly raised after removing the slag, you have chosen the optimal welding current. If you finish it
with a roughing wheel, the bare metal appears.
Welding current too weak or too strong: If the seam is only on the surface of the workpiece, the
connection between the materials is not strong enough. This means that you have selected a
welding current that is too weak. If the welding current is too high, too much material is melted
from the workpiece. Thinner workpieces can even burn through.
When igniting, do not hold the electrode anywhere on the workpiece, but always in the area of the
later weld seam. This way you avoid cracks and binding errors and the weld seam becomes more
even.
Note: Before working on the actual workpiece, first gain some experience on residual or test
pieces.
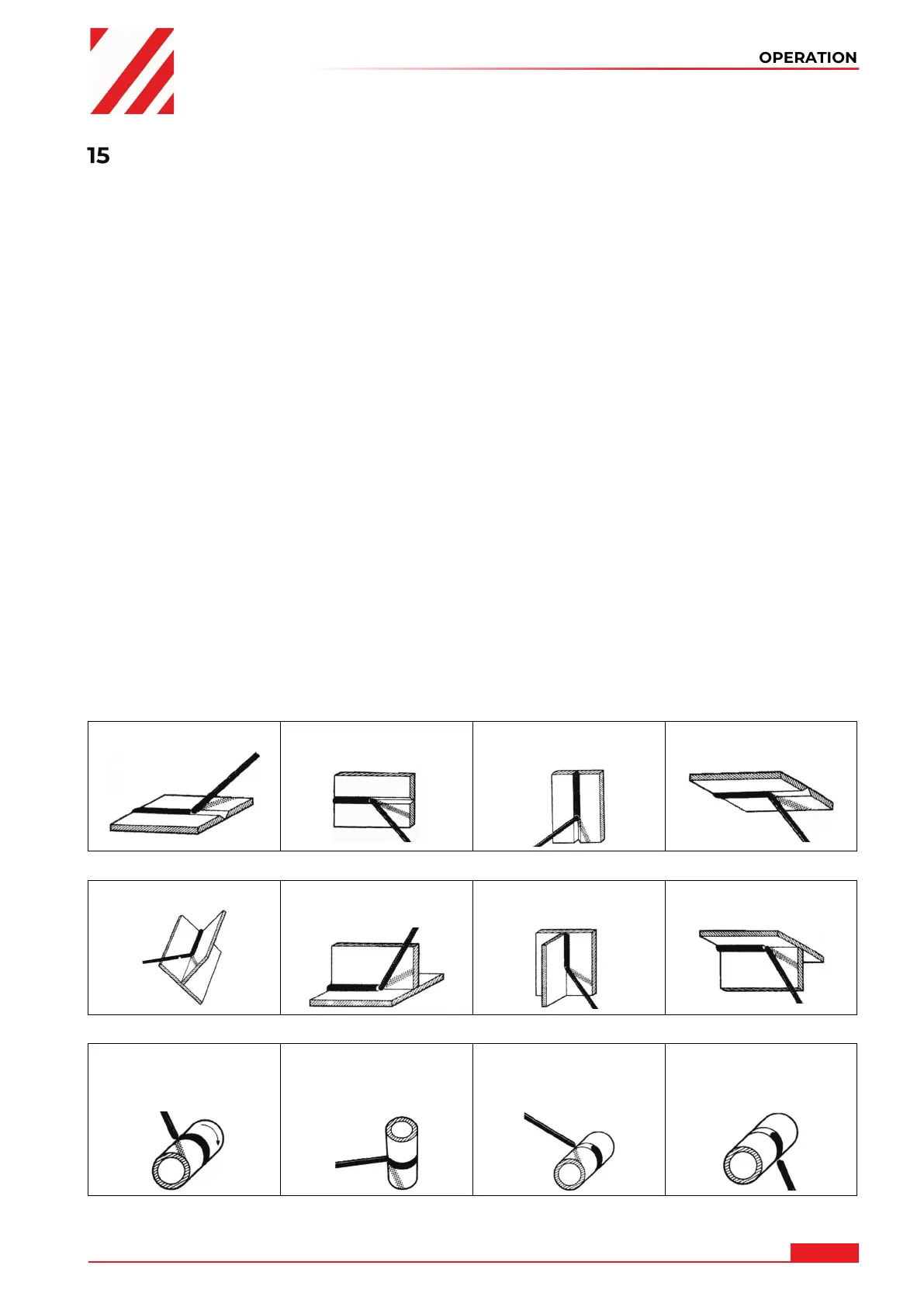
15.1.1 Weldseams
Butt welds:
PA – Flat position
PC – Transverse
position
PG – Vertical down
position
PE – Overhead
position
Fillet welds:
PA – Flat position
PB – Horizontal-
downhand position
PG – Vertical down
position
PD – Horizontal-
overhead position
Pipe-Butt welds:
PA – Pipe: rotated
Axis: horizontal
Welding: flat
PC – Pipe: fixed
A
xis: vertical
Welding: transverse
PF – Pipe: fixed
Axis: horizontal
welding: vertical up
PG – Pipe: fixed
Axis: horizontal
Welding: vertical down
Bekijk gratis de handleiding van Holzmann EISA160-MINI, stel vragen en lees de antwoorden op veelvoorkomende problemen, of gebruik onze assistent om sneller informatie in de handleiding te vinden of uitleg te krijgen over specifieke functies.
Productinformatie
| Merk | Holzmann |
| Model | EISA160-MINI |
| Categorie | Niet gecategoriseerd |
| Taal | Nederlands |
| Grootte | 6917 MB |







