Thames & Kosmos Genetics & DNA Lab handleiding
Handleiding
Je bekijkt pagina 18 van 52
The way that features were distributed
was still unclear to Mendel. But on this
topic, he had a few more ideas. After all his
experiments, it suddenly became clear as
day to him that each partner only passes
on one copy of each program to the
offspring and not all the copies. That
makes sense, because otherwise the
number of programs would double with
each generation.
Luckily, it is much more orderly than that:
Only one of two possible programs passes
from the parents to the children — so each
of the offspring logically ends up with two
copies again.
How features
are passed on
YOU WILL NEED
→ colored plastic chips
Possible
combinations
These are the
parent plants’
programs.
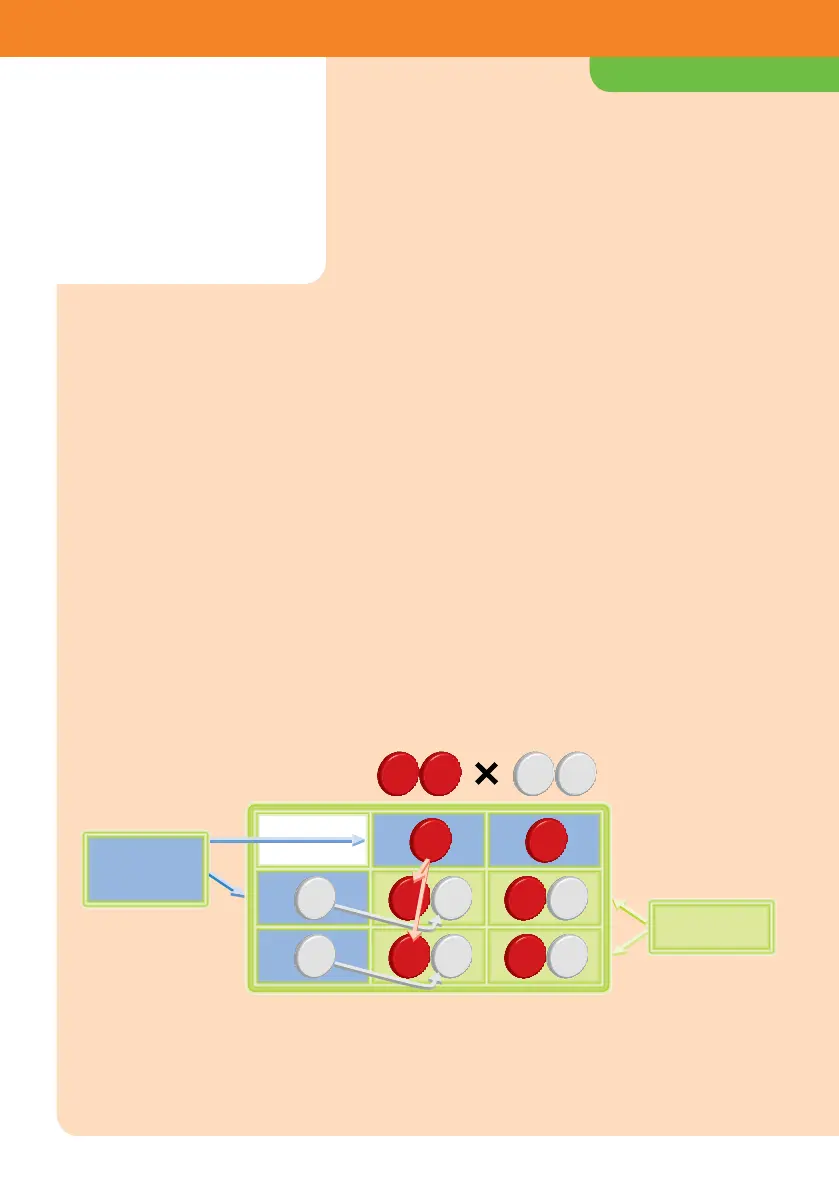
The X indicates that pea plant 1 (red-red) is
crossed with pea plant 2 (white-white). From
that crossing, we get four possible pea plant
offspring, all with red flowers.
Now we can explain which four combinations
of the programs can arise from two different
pea plants when they are crossed.
HERE’S HOW
1. For the first pea plant breeding exercise,
one pea should have two programs for red,
and the other should have two for white.
By placing the colored chips in the grid
drawing below, you can easily figure out all
possible combinations.
2. In each case, one program from one parent
is crossed with one program from the
other.
Because we are dealing with peas here, all
the offspring are red, since the program for
red color always dominates. Not a trace of
white to be seen — at least, not from the
outside, by looking at the flower color.
16
EXPERIMENT 8
Bekijk gratis de handleiding van Thames & Kosmos Genetics & DNA Lab, stel vragen en lees de antwoorden op veelvoorkomende problemen, of gebruik onze assistent om sneller informatie in de handleiding te vinden of uitleg te krijgen over specifieke functies.
Productinformatie
| Merk | Thames & Kosmos |
| Model | Genetics & DNA Lab |
| Categorie | Niet gecategoriseerd |
| Taal | Nederlands |
| Grootte | 20798 MB |







