Nord Modular G2 handleiding
Handleiding
Je bekijkt pagina 280 van 291
14. Synthesis basics: Other synthesis and modulation methods NORD MODULAR G2 V1.4x
Page 280
OTHER SYNTHESIS AND MODULATION METHODS
FM
SYNTHESIS
FM stands for Frequency Modulation and is a method for adding harmonic and inharmonic frequencies
to a sound by modulating its frequency with another signal. A signal routed to an FM input on a module
affects the pitch by modulating it linearly in the frequency scale as opposed to Pitch modulation where
you modulate the frequency in the note scale. The difference in frequency between carrier and modulator
wave determines the density of partials in the sound. The level of the modulator wave determines the
total bandwidth of the sound.
The practical result of FM is often a “metallic” or “bell” type of sound. The most common wave to do
FM on is a pure sine wave, but any type of waveform can be used, both as modulator and carrier (wave
to be modulated). Complex waveforms will generate more frequencies than simpler waves.
AM
SYNTHESIS
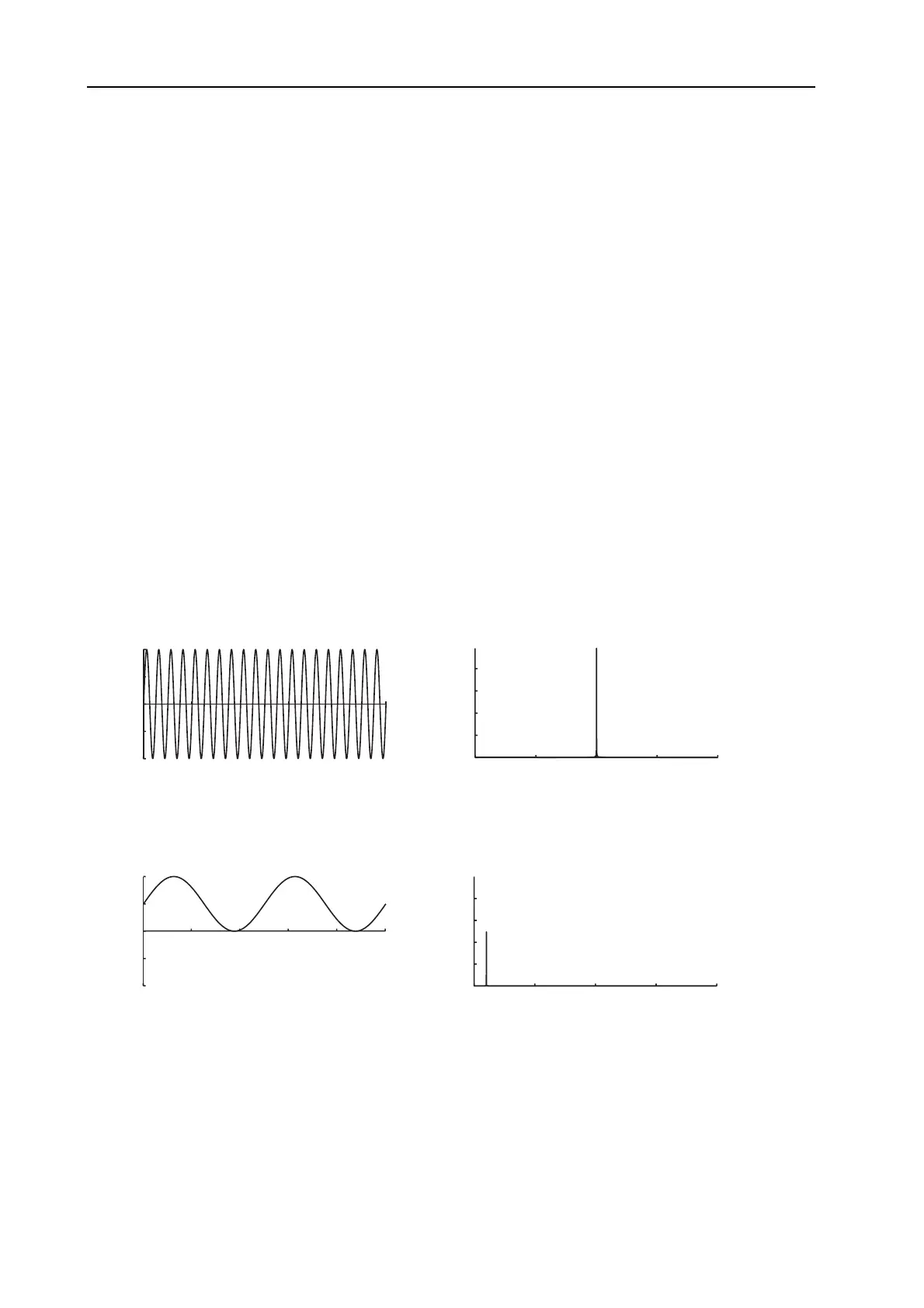
AM stands for Amplitude Modulation and is a method for adding frequency bands by modulating the
amplitude of the carrier wave. To illustrate what amplitude modulation actually does to a sound, we have
created a simple example with two sine waves, one carrier and one modulator. The graphs to the left show
the amplitude as a function of time, and to the right the amplitude as a function of the frequency.
time
amplitude amplitude
frequency
Fig 1. AM Carrier wave
f
C
time
amplitude amplitude
frequency
Fig 2. AM Modulator wave
Bekijk gratis de handleiding van Nord Modular G2, stel vragen en lees de antwoorden op veelvoorkomende problemen, of gebruik onze assistent om sneller informatie in de handleiding te vinden of uitleg te krijgen over specifieke functies.
Productinformatie
| Merk | Nord |
| Model | Modular G2 |
| Categorie | Niet gecategoriseerd |
| Taal | Nederlands |
| Grootte | 60689 MB |







